Corresponding authorProf. Yingbo Dong
Communication UnitSchool of Energy and Environmental Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing
DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135457
Image Summary
Results Profile
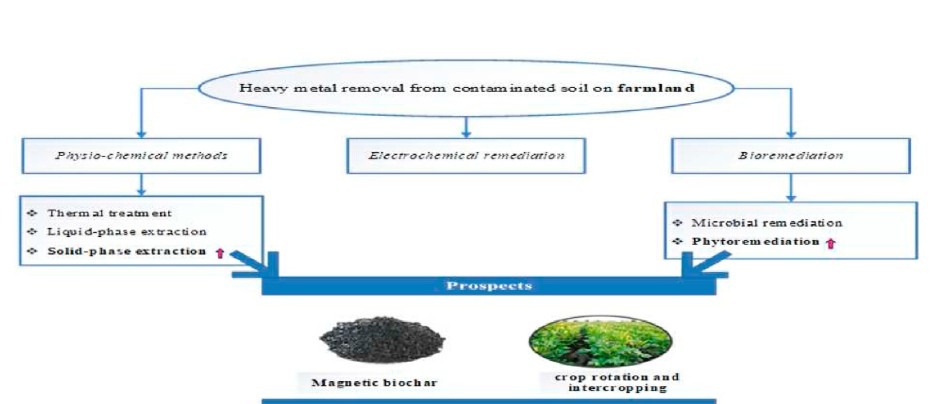
Recently, Ziwei Wang, a master student of the group, published a paper entitled "Technologies for removing heavy metal from contaminated soils on farmland: A review" in Chemosphere (IF=8.943). This paper reviews the current status of heavy metal pollution on farmland and the progress of removal technologies, and provides an in-depth analysis and comparison of remediation technologies from three aspects: physicochemical, electrochemical and bioremediation, which provides a reference and direction for the selection of remediation technologies in the agricultural field in the future.
Abstract
With the rapid development of industrialization and agricultural intensification and scale, the problem of heavy metal pollution in agricultural fields has attracted widespread attention. There are various methods to remediate heavy metal contaminated soils, but the sources and degree of contamination in agricultural soils are more complex and therefore have higher requirements for the selection of remediation technologies. In this paper, the current situation of heavy metal pollution in agricultural fields and the research progress of removing heavy metals from soils are discussed in detail, and the remediation technologies are analyzed and compared in depth from three aspects: physicochemical, electrochemical and biological remediation, which provide references and directions for the selection of remediation technologies for heavy metal pollution in agricultural fields in the future. It was found that the presence pattern of soil heavy metals is an important reference for the selection of soil remediation methods; in practical applications, the use of magnetic biochar for phytoremediation and removal of heavy metals from agricultural soils has good potential for development. The remediation of agricultural land through crop rotation or intercropping can not only achieve remediation while producing, but also optimize the soil environment. However, phytoremediation requires a high degree of pollution in the soil environment, and the selection of plant species is the key to phytoremediation, and in-depth research is needed in the future to improve the tolerance of plants to heavy metals. Magnetic biochar is an ideal material for soil remediation because it has relatively short remediation time and can be reused. The binding mechanism of magnetic biochar with heavy metals and the effect on soil microorganisms need to be further investigated in the future.
Author

Ziwei Wang, a master's student in Environmental Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Class of 2021, is engaged in the research of soil heavy metal remediation. Finally, congratulations again to Ziwei Wang, a master's student, and wish the graduate students of the subject group to keep innovating and making further efforts to achieve fruitful results.
Source: Environmental Biotechnology and Environmental Materials Development Team Public

