First author:Zheng Lili
Corresponding authorProf. Linhai
Communication UnitSchool of Energy and Environmental Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing
DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127457
✦Image Summary✦
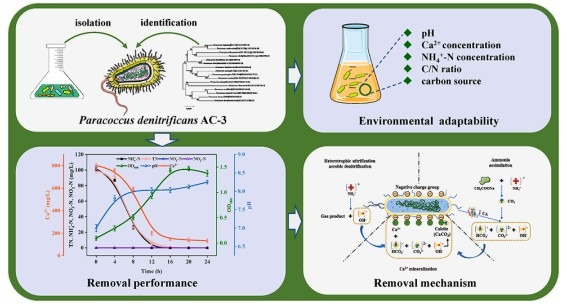
✦Results Profile✦
Recently, Lili Zheng, a PhD student in the group, published a paper in the international SCI journal Bioresource Technology (IF=9.642) entitled "Simultaneous removal of high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and calcium by the novel strain Paracoccus denitrificans AC-3 with good environmental adaptability". In this study, a novel strain of heterotrophic nitrifying aerobic denitrifying (HNAD) bacteria with significant carbonate precipitation capacity and good environmental adaptability was isolated forParacoccus denitrificans AC-3 simultaneously removes ammonia nitrogen (NH4+-N) and calcium ions (Ca2+) performance was evaluated. The nitrogen balance analysis was used to determine the performance of strain NH4+-N removal pathway, and by monitoring carbonic anhydrase (CA) secretion and analyzing Ca-rich2+and without Ca2+The pH of the system, carbonate (CO32-) and bicarbonate (HCO3–) concentration was explored for the variation of Ca2+precipitation pathway. The strains were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy energy spectroscopy (SEM-EDS)Paracoccus denitrificans AC-3-induced Ca2+The crystal structure and morphology of the precipitation. This work provides an opportunity to treat industrial wastewater with high concentrations of NH4+-N and Ca2+provides a new microbial resource and reveals that HNAD precipitates Ca2+The pathways and mechanisms of the
✦ Abstract ✦
In this study, a strain was isolated that was sensitive to high concentrations of NH4+-N and Ca2+Bacteria with strong removal efficiencyParacoccus denitrificans AC-3, a strain with a wide pH range and a high NH4+-N, Ca2+showed good environmental adaptability at the concentration of Nitrogen balance analysis showed that NH4+-N removal pathways include assimilation by 80.12% and HNAD by 16.60%. Ca2+By working with CO32-and HCO3–The formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and removed, while CO32-and HCO3–By strainParacoccus denitrificans AC-3-secreted CA-catalyzed CO2CA and HNAD are generated by hydration. CA and HNAD provide an alkaline environment for carbonate precipitation. The resulting CaCO3It exists in the form of calcite and exhibits a unique morphology and elemental composition.
✦Author✦

Lili Zheng is a PhD student in Environmental Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Class of 2020. She is engaged in the research of microbial water remediation and biotechnology research and development. She has participated in projects such as pollution source survey of drinking water sources in Beijing. Finally, we congratulate Dr. Zheng Lili once again and wish the graduate students of the group to keep innovating, to make further efforts and to achieve fruitful results.
Source: Environmental Biotechnology and Environmental Materials Development Team Public

